Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the different types of central heating and cooling systems is essential for making informed decisions.
- Energy efficiency, installation costs, and climate suitability are critical factors to consider.
- Recent advancements in HVAC technology have led to improved comfort and reduced energy consumption.
Introduction
As technology continues to advance, homeowners increasingly expect HVAC systems that combine efficiency, reliability, and convenience. Innovations in heating and cooling solutions enable more intelligent energy management and precise climate control. These developments not only improve day-to-day comfort but also contribute to long-term cost savings and environmental responsibility. Modern homeowners face numerous choices when selecting central heating and cooling systems. These decisions directly impact energy bills, comfort levels, and ecological sustainability for years to come. Exploring options such as central ducted heat pumps reveals just how much the HVAC industry has advanced, with new systems now offering both powerful performance and high energy savings.
Before choosing any system, it’s essential to assess how each type operates, its compatibility with the home’s structure, and how it performs across different climates. These considerations ensure that your investment provides comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for your unique living situation.
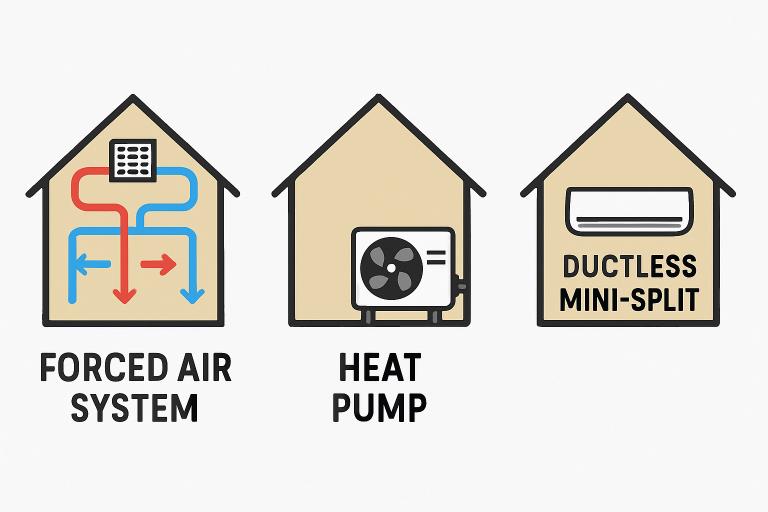
Types of Central Heating and Cooling Systems
Today’s homes typically utilize one of three major types of central systems, each with its own advantages and drawbacks:
- Forced-air systems:These systems use ducts and vents to distribute conditioned air rapidly throughout the home. They’re highly effective for controlling indoor climates and allow for the integration of air filtration and humidification options.
- Heat Pumps:Versatile and energy-efficient, heat pumps function as both heaters and coolers by transferring heat to and from the outdoors. Particularly in milder climates, they offer substantial utility savings while effectively managing indoor temperatures.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems:Ideal for older homes or new additions without ductwork, these systems offer individualized zone control, enhancing comfort and minimizing energy waste.
Every option has its unique merits, so understanding which type fits your home’s requirements—both structurally and financially—is the first step in making an optimal choice. For homes located in extreme climates or with existing ductwork, specific systems may prove far more suitable than others. Additionally, maintenance needs and long-term operating costs can significantly influence the decision-making process.
It’s also worth consulting consumer-focused resources such as Consumer Reports to compare system performance, reliability, and user reviews for a long-term ownership perspective.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Energy efficiency isn’t just about saving money—it’s about reducing your environmental footprint, too. Thanks to new technologies, systems like heat pumps have revolutionized the market, providing up to 76% less heating energy consumption, which can result in considerable cost reductions and help to address climate change. According to experts, proper selection can significantly transform your home’s energy dynamics, and high-efficiency systems may be eligible for tax credits or rebates in certain regions.
Modern advancements mean that even traditional forced air systems now come with improved energy performance features, such as better insulation and variable-speed motors. Ductless systems, on the other hand, excel in tightly sealed homes where energy waste from ducts can be a concern.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
Costs for installation and long-term maintenance vary extensively by type and scale. For instance, a standard air-source heat pump can range from $6,500 to $12,000 in installation expenses, while geothermal (ground-source) systems—renowned for their long-term efficiency—start at around $18,000 and can cost up to $35,000. Forced-air and ductless systems usually cost less upfront but may require more frequent maintenance, especially for complex ducting or filters.
Regardless of system choice, preventative maintenance is key. Annual inspections, filter replacement, and ensuring seals and ducts are intact not only extend the lifespan of the system but are also crucial to maintaining efficiency and preventing breakdowns.
Climate Considerations
The choice of a home heating and cooling system is strongly influenced by where you live and the typical weather patterns in your region. In areas that experience harsh winters, systems designed to perform efficiently in low temperatures—such as dual-fuel setups or cold-climate air-source heat pumps—are particularly effective, ensuring consistent warmth without excessive energy use. Conversely, homeowners in moderate or mixed climates can often rely on standard heat pumps or ductless mini-split systems, which deliver reliable heating and cooling while maintaining high energy efficiency. Beyond climate considerations, local utility incentives, rebates, and regulations can significantly affect both upfront costs and long-term savings. Evaluating these factors alongside performance requirements ensures a system tailored to your home’s environment and financial goals.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have transformed modern HVAC systems, making them more efficient, responsive, and user-friendly than ever before. Variable-speed compressors and fans intelligently adjust their output in real-time according to heating or cooling needs, minimizing energy waste while maintaining consistent indoor comfort. Smart thermostats and Wi-Fi-enabled controls enable homeowners to remotely monitor, schedule, and adjust their systems, providing unmatched convenience and optimized performance. Additionally, many contemporary systems include advanced filtration and air purification features, which help reduce allergens, dust, and other airborne contaminants. This not only enhances overall indoor air quality but also supports healthier living environments, particularly for individuals with respiratory sensitivities. Together, these innovations create a more energy-efficient, comfortable, and health-conscious home experience.
Conclusion
Selecting the proper central heating and cooling system requires more than simply comparing brands—it involves understanding how each option aligns with your home’s specific needs. Homeowners should assess factors such as system capacity, long-term energy usage, upfront installation requirements, and ongoing maintenance demands. Evaluating how well a system performs in your local climate is equally essential, as efficiency can vary based on temperature and humidity levels. Today’s advanced HVAC technologies, including smart thermostats and variable-speed components, provide greater control, quieter operation, and reduced energy waste. With a thoughtful approach, homeowners can enjoy year-round comfort, lower utility bills, and a reduced environmental footprint while ensuring their system performs reliably for years to come.